There is no doubt that town centres were among the places hardest hit by the effects of the pandemic, worsening a crisis already felt in many European highstreets. Nevertheless, many elements of these town centres can be potential engines for attracting new residents or creating new economic opportunities for small shops and other commercial activities.
Coming from a big city, the most striking aspect when you arrive in a small or medium-sized town is the silence, the slowed-down activity compared to the symphony of horns, buses and incessant background noise that characterises a day spent in a larger urban context. This is particularly true when visiting the partner cities in URBACT networks that deal with the revitalisation of small historic centres, such as City Centre Doctor. The network has represented in recent years one of the main arenas of dialogue for small and medium-sized European municipalities committed to finding common solutions to a plurality of cross-cutting issues to design the small liveable cities of the future.
Environmental care, the promotion of tourism, the revitalisation of urban spaces, economic growth: these are just a few of the main concerns for cities whose centres were hit first by the economic crisis and then by Covid, with each new crisis increasing the risk of depopulation.
Much smaller than nearby Treviso or Venice, San Donà di Piave (IT), with 40 000 inhabitants, is the right size to be able to experiment with shared methodologies for the recovery and improved quality of public spaces, creating spaces where new forms and methods of innovation and participation can be tested. It is perhaps no coincidence that this municipality is the first in Italy to have launched a Department for Participatory Urban Regeneration, with clear mention of the URBACT Local Group as a long-term tool to make the collaborative methodologies promoted by the European programme part of the regular activities of the municipality.
Compared to bigger cities, it is easier to focus attention on these issues in small towns where social cohesion is stronger and local government actions can be more incisive in revitalising social spaces, in order to recreate a new community spirit. It is also in small towns that important approaches can be developed to make centres more liveable and inclusive, with valid lessons for larger urban contexts too.
The solutions, and food for thought, produced by City Centre Doctor and other URBACT networks on the theme of small city centres have animated national and European debates on the implementation of European and global Urban Agendas, as well as contributing to the new European cohesion policy. Here are five key lessons:
1. To revitalise a city centre, think about what you want to do with the urban space
Many cities focus on using empty spaces for parking, but the experience of cities such as Amsterdam, Utrecht, and Copenhagen teaches us that reducing the space allocated to cars can be a decisive contribution to making a city more vibrant and liveable.
The use of large spaces, such as squares, for a variety of functions is the ideal way to revitalise a city, whether large or small, perhaps even providing original uses: a playground, an urban beach, or a place for art installations, yoga, or music for young people.
In small towns, it is possible to return to the concept of the square and enrich it with new uses. The same is true for streets, which are transformed into temporary open-air markets during neighbourhood festivals in Belgian cities, or given back to the citizens to pedal, walk, meet or eat together in Medina del Campo (ES).
It's not just a matter of pedestrianisation, but also of making the streets more beautiful: covering them with marble, as in Portugal, or with street artworks, as in San Francisco or in Quito, Ecuador, where a work of tactical urbanism was created at the occasion of the Habitat III Conference in 2016.
2. It won't be the big stores that save the historical centres, but small-scale, high quality commerce
Can bringing Primark or McDonald's into a small town make it more attractive? Not really, especially if you think about the economic and social sustainability of the whole operation. Instead, create the conditions to make historic centres a framework in which quality commerce can grow, bringing creativity and value to small towns, starting with a redefinition of public spaces to make them liveable, walkable, and attractive. Heerlen has tried this with the widespread use of street artwork, making the Dutch town an open-air museum of urban art – certified as a good practice by the URBACT programme.
But street art alone is not enough. Experimenting with new systems of rules to encourage creative entrepreneurship, for example by making it possible to open temporary stores or encouraging young people to open new businesses with specific training actions and exemption from paying local taxes for two years, are some elements of the strategies revitalising cities in Belgium or Ireland, for example. Solutions include Cork’s ‘Streetwise’ programme or Antwerp's ‘Pop up to date’ initiative, another URBACT good practice.
Many small centres are also focusing on maintaining local stores and enhancing activities such as craft breweries and bars. They put the focus on quality and reasoned use of public spaces, giving inhabitants the perception of an attractive and liveable place.
"A place needs to be cool, but you only create ‘coolness’ if you create better public spaces and properly support the work of entrepreneurs," comments Wessel Badenhorst, City Centre Doctor lead expert.
Proximity shops proved their importance during the lockdown, helping revive community spirit in many towns and villages. What happened in 2020 is a reminder of the importance of this particular category of commercial activities, some of which innovated their offers to contrast the rise of online commerce with more personalised customer service.
3. Kicking cars out of downtowns to make them more liveable
In small towns, you can still see children riding their bikes on sidewalks, but residents are often dependent on cars to access basic services. There is no doubt that the longer cars stay out of town centres, the more attractive they become.
The issue of mobility in small towns concerns not only the way people move from one place to another, but also the system of transporting goods, especially now that online platforms and courier lorries are revolutionising the way we shop, even in the smallest towns.
Reducing pollution by organising mobility and supply systems differently is a key solution to improving the way people perceive the spaces around them. For example, the use of cargo bikes instead of polluting trucks to create delivery systems that are environmentally friendly and close to the end user is becoming increasingly popular in a sector that, despite a lack of major innovative improvements, can act strongly on established habits of the various links in the chain.
Cure people from car dependency: an assumption that becomes the cornerstone of structured and collaborative actions and policies, especially in small towns.
4. Making young and old the protagonists of change in historic centres
Young people and the elderly are two social groups tied more closely than others to historic town centres. For young people who do not own a car, the historic centre can become part of their identity, with the consequence that if there are few local activities, they grow up hoping to leave, abandoning their small centre. Making young people protagonists of their hometown’s future is a solution to stop them wanting to ‘escape’.
The mayor of Idrija, Slovenia, asked local young people to indicate a series of actions to be carried out in different parts of their town. Unexpectedly, rather than asking for disruptive, chaotic actions, they asked for re-appropriation of spaces, activities in the squares such as music and dance performances, or playing with skateboards. This proved that it is not just bars that make young people stay in a place, but rather the freedom to do their own thing. This was also true in Amarante, Portugal, where young people were able to organise a week of events on the theme of citizenship. "Young people are the ones who implement change in the inner cities," says Wessel Badenhorst.
As for the elderly, and others who are unable to drive, access to healthcare and social services becomes a key factor in their ability to live in the area.
Udine’s Playful Paradigm – a good practice shared with other medium-sized city partners thanks to URBACT – is one solution to help counter depopulation and promote social cohesion. The approach fosters links between different segments of the population through programmes and initiatives that strengthen people’s sense of belonging to the place they live, and promote its quality of life. Better urban planning starts from places and spaces designed and shared with people: Jane Jacobs' teaching is even more valid in centres where different parts of the population must cooperate to keep alive the branch of the tree on which they are sitting.
Collaboration among residents of different generations during the Covid crisis is a perfect example of how communities can be resilient in small centres: a lesson for cities to implement in wider, integrated policies for social welfare, urban planning and liveability.
5. Making inhabitants proud of the place in which they live
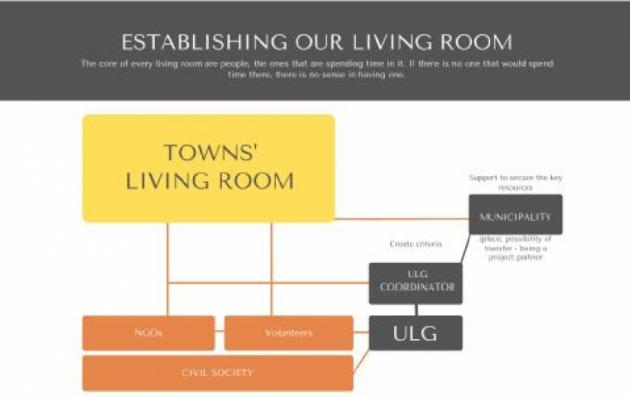
Creating trust among people to change the collective perception of small historic centres is a political and cultural operation that participatory processes can help to revive by giving inhabitants a more complete picture of the in which place they live. By setting up URBACT Local Groups, and exchanging with other URBACT towns on the challenges of revitalising their historic centres, cities gain ideas and possible solutions not only to help manage, but also promote, their town centres.
Though the history of a small centre cannot be changed, the trends and prospects for future development can be oriented to start again from an act of co-creation that makes people protagonists of the processes of change and management of their town centres. "No one owns the cities," said Jane Jacobs – and this is more true than ever in the centres, where collective action can lead to a collective re-appropriation of governance, in which everyone can have a decisive role. Making people proud to participate in the future development of their community also favours the visibility and attractiveness of small towns, the silent engine of a Europe that grows thanks to the vital and vibrant places that contribute original visions and practices in the time of big cities.